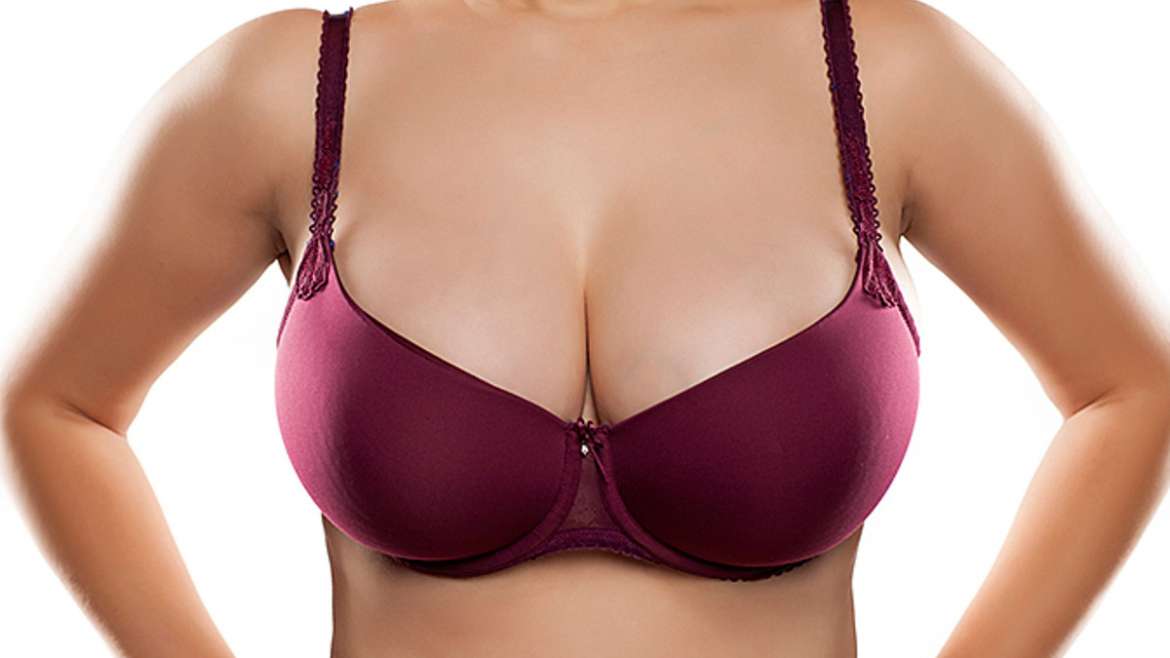
Breast Augmentation
It is the surgical procedure that serves to enhance the size and shape the woman’s chest.
Breast augmentation requires careful evaluation of breast morphology and chest wall anatomy. It is necessary to carry out a pre-operative study consisting of mammograms, laboratory tests and cardio-respiratory assessment, and to assess the characteristics of the patient: width of the glandular base, adequate skin coverage and capacity for anterior distension due to skin traction and distance. from the areola and nipple to the inframammary groove under maximum tension. Furthermore, it is important to assess the long-term evolution and dynamics of the implant and soft tissues.
Other variables to consider are the size and shape of the implant, the approach, and the location and dimensions of the pocket; in addition to assessing the shape of the breast and whether it is sagging, to associate the lifting of the breast prior to the placement of the prostheses (Mastopexy). Special care should be taken in cases of asymmetric breasts and in those with thin skin coverage, poor lower pole or ptosis.
How is the mammoplasty intervention?
The method to insert and place the breast implant will depend on its anatomy and the surgeon’s recommendations. The implant can be placed through an incision in the submammary fold, around the areola or through the axillary route, trying to make the resulting scars as discrete as possible. Once the incision is made, the surgeon will dissect the breast tissue and skin to create a pocket, where the prostheses will be placed, directly behind the mammary gland (retroglandular) or behind the muscular wall of the thorax pectoralis major (retropectoral).
The advantage of the latter is that it is more natural since the breastplate hides and qualifies it; in addition to being the best option in cases where the patient has very little gland, although it can be more painful the days after surgery.
To avoid accumulation of blood or serousness, which favor capsular contracture, routine drains are left. In some cases, breast augmentation may be accompanied by a reduction in areolar size. Mammoplasty, which lasts between 1 and 2 hours approximately, is usually performed under local anesthesia with sedation; although in some cases general anesthesia is administered, requiring in this case a 24-hour hospitalization. Sensitivity is fully preserved, as is the role of the breast for lactation.